
Title: The Hypothetico-Deductive Process: Applying Scientific Reasoning in Real Life
Introduction:
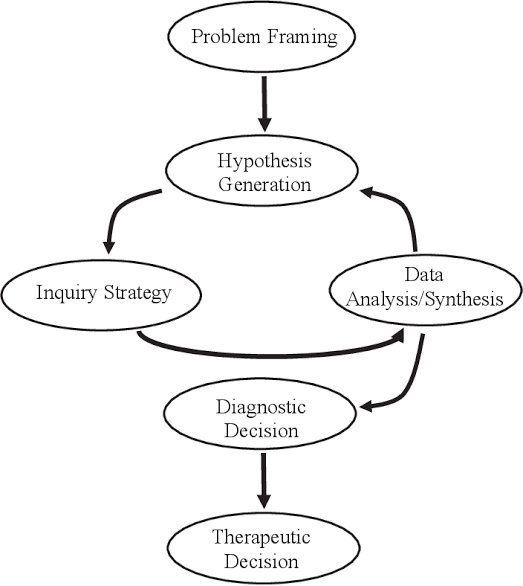
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of the hypothetico-deductive process and its application in real-life situations. The hypothetico-deductive process is a fundamental framework used in scientific inquiry and problem-solving. By understanding this process, we can effectively tackle complex problems and make informed decisions based on logical reasoning and evidence.
1. Formulating a Hypothesis:
To begin the hypothetico-deductive process, we first encounter a problem or question that requires investigation. Let’s consider an example from the field of healthcare: A hospital observes a sudden increase in patient infections post-surgery, and they suspect that it may be due to a specific medical device.
2. Gathering Observations and Data:
Next, we gather relevant observations and data related to the problem. The hospital collects information about the patients, their surgeries, and the medical device used. They also analyze infection rates, patient outcomes, and any other relevant variables.
3. Formulating a Hypothesis:
Based on the collected data and observations, the hospital formulates a hypothesis. For instance, they hypothesize that the increase in post-surgery infections is directly correlated with the use of the specific medical device.
4. Predicting and Testing:
The next step is to make predictions based on the hypothesis and design experiments or interventions to test those predictions. In our example, the hospital decides to compare infection rates in two groups: one group where the device is used and another group where an alternative device is used.
5. Data Analysis and Conclusion:
After conducting the experiments, the hospital collects and analyzes the data. They compare the infection rates between the two groups and look for any statistically significant differences. If the data supports the hypothesis, it strengthens the evidence that the medical device is indeed linked to the increased infections.
6. Drawing Conclusions and Decision Making:
Based on the data analysis, the hospital draws conclusions. If the hypothesis is supported, they may decide to discontinue the use of the device, implement alternative measures, or further investigate the underlying causes of the issue.
7. Iteration and Further Refinement:
The hypothetico-deductive process is often iterative. If the conclusions do not align with the hypothesis, the hospital may need to revise their initial assumptions, develop new hypotheses, and conduct further experiments to gain a deeper understanding of the problem.
Conclusion:
The hypothetico-deductive process is not limited to scientific research alone; it can be applied to various real-life situations where logical reasoning, evidence, and problem-solving are crucial. By following this process, we can approach complex problems systematically, make informed decisions, and continuously refine our understanding of the world around us.
Real-life Example:
In the field of environmental conservation, a team of researchers may use the hypothetico-deductive process to investigate the impact of a specific farming practice on water quality in a nearby river. They would collect water samples, analyze pollutant levels, develop hypotheses about the farming practice’s influence, design experiments or interventions to test those hypotheses, analyze the data, draw conclusions, and inform decision-making regarding sustainable farming practices.
By applying the hypothetico-deductive process, researchers can contribute to evidence-based solutions and create positive change in real-life contexts.