

Introduction:
Welcome to our technology blog where we explore the intricate workings of computer systems. In this article, we delve into the fundamental concepts of primary memory and secondary memory, highlighting their differences and roles in storing and accessing data. Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending computer hardware and data storage. So, let’s dive in and unravel the distinctions between primary memory and secondary memory.
—
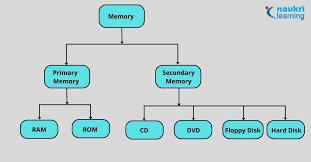
1. Primary Memory: The Core of Computing
Primary memory, also known as main memory or primary storage, refers to the internal memory of a computer system. It plays a vital role in the execution of programs and the temporary storage of data that is actively being processed by the CPU (Central Processing Unit). Primary memory is built using electronic components, allowing for high-speed data access and retrieval.
#PrimaryMemory #ComputerHardware #RAM
2. RAM: The Backbone of Primary Memory
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the most common form of primary memory in modern computer systems. It is a volatile memory type, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is powered off. RAM holds the operating system, software applications, and data that are actively used by the CPU. It provides fast access to data, allowing for efficient execution of tasks.
#RAM #PrimaryMemory #DataStorage
3. Secondary Memory: Long-Term Data Storage
While primary memory is essential for immediate data access, secondary memory serves as a long-term storage solution. Unlike primary memory, secondary memory retains its contents even when the computer is powered down. It allows for the storage of large amounts of data that can be accessed and retrieved as needed.
#SecondaryMemory #DataStorage #HardDrive
4. Hard Drives: The Common Secondary Storage Medium
Hard drives are the most widely used secondary storage devices in computers. They consist of magnetically sensitive platters that store data, along with read/write heads that access and modify the information. Hard drives provide ample storage capacity but have slower access speeds compared to primary memory.
#HardDrive #SecondaryMemory #DataStorage
5. Memory Hierarchy: Balancing Speed and Capacity
The concept of a memory hierarchy encompasses the different levels of memory within a computer system. Primary memory, with its high speed and low capacity, resides at the top of the hierarchy. Secondary memory, offering larger storage but slower access, occupies the lower levels. The memory hierarchy ensures a balance between data access speed and storage capacity, optimizing overall system performance.
#MemoryHierarchy #PrimaryMemory #SecondaryMemory
6. Caching: Bridging the Gap
Caching is a technique used to bridge the speed gap between primary and secondary memory. It involves temporarily storing frequently accessed data in a cache, which is a small but faster memory unit. Caching minimizes the need to retrieve data from slower secondary memory, enhancing system performance.
#Caching #PrimaryMemory #SecondaryMemory
—
Conclusion:
Primary memory and secondary memory are integral components of computer systems, serving distinct purposes in data storage and retrieval. Primary memory, represented by RAM, provides fast access to data actively used by the CPU. On the other hand, secondary memory, typically in the form of hard drives, offers long-term storage capacity. Understanding the differences between these memory types and their roles in the memory hierarchy is essential for comprehending computer hardware and optimizing system performance.